Heat stress - Overheating during work
Heat stress occurs when the body becomes overheated and cannot cool down effectively. This can happen in hot environments, especially when people perform physically demanding work or are exposed to high temperatures for extended periods.
What is heat stress?
The body normally regulates temperature through sweating, but in hot conditions, the natural cooling process can become overwhelmed, leading to heat stress.
Symptoms of heat stress may include:
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Nausea
- Cramps
- Rash
- Overheating
FatigueIf the condition worsens, it can develop into more serious health issues such as heat exhaustion or heat stroke, which can be life-threatening.


Risk Factors:
- High humidity
- Poor ventilation
- Wearing heavy protective equipment that prevents sweat evaporation
- Working in hot and enclosed areas, such as industrial facilities or outdoors in direct sunlight
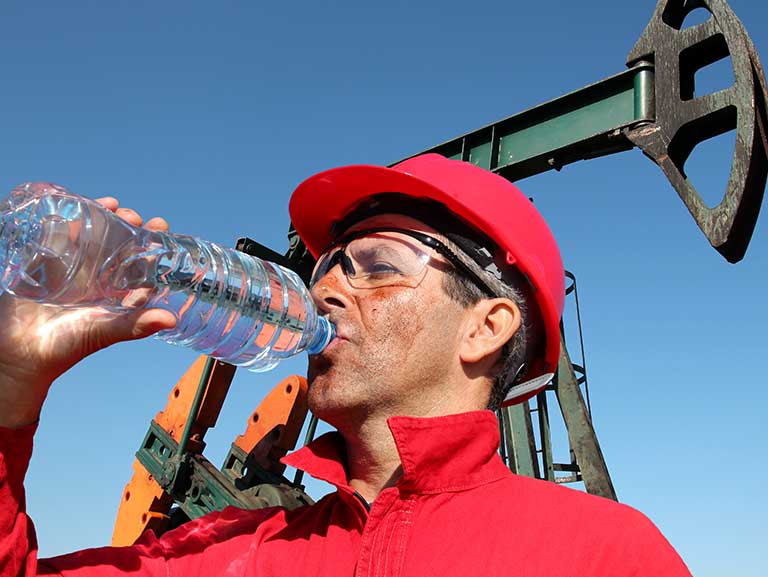
To avoid heat stress, it is important to:
- Take regular breaks
- Drink plenty of water
- Wear breathable clothing
- Work in shaded or well-ventilated areas
Protection against heat through temperature management
Wenaas' approach to protecting against heat stress focuses on combining the right materials, work routines, and personal protective equipment (PPE) to keep the body cool and protected in demanding, high-temperature environments.
This system is built on multiple layers of measures:
- Moisture-wicking base layers:
The foundation of heat protection is wearing garments that transport sweat away from the skin. Base layers made from specially woven polyester or merino wool help keep the skin dry, reducing the risk of overheating.These materials are designed to be lightweight, breathable, and quick-drying, which is essential for maintaining the body's natural cooling system in hot conditions. - Breathable mid-layers:
Mid-layers should be lightweight and breathable to ensure good airflow around the body. Materials such as mesh or technical fabrics with high breathability help to ventilate warm air and moisture while providing a protective buffer against the sun's heat.This layer supports the body's natural temperature regulation by allowing proper air circulation, preventing heat from accumulating on the skin. - Lightweight and breathable outerwear:
Outerwear should be lightweight, breathable, and made from materials that reflect heat. These garments must allow heat to escape while protecting the wearer from external factors such as direct sunlight or hot air.Breathable outerwear with built-in ventilation openings can help reduce heat buildup inside the clothing, providing greater comfort when working in hot environments. - Cooling personal protective equipment (PPE)
Airy, ventilated, or cooling equipment can help reduce body temperature in hot conditions. Equipment that retains cold, promotes evaporation, or helps draw heat away from the body is preferred.Using gloves, helmets, and shoes with some form of ventilation or cooling technology can help reduce heat stress.
In addition, the key points are:


- Awareness and training
Training on the symptoms of heat stress, such as dizziness, nausea, and fatigue, is essential. Workers must be able to identify early signs of overheating and know when to stop working and cool down.A well-informed workforce is better equipped to prevent dangerous situations.


- Work schedule planning
Adjusting Work Schedules in Extreme HeatIn extreme heat conditions, work schedules should be adjusted to avoid the hottest parts of the day. Tasks should be carried out early in the morning or late in the afternoon when temperatures are lower.If this is not possible, breaks and shaded areas should be easily accessible for all workers. For those working in hot environments such as engine rooms, where shade is not an option, it is crucial to take frequent breaks away from the heated work area.


- Regular breaks – avoid dehydration
Maintaining hydration is crucial to preventing heat stress. Workers should drink water regularly, preferably before they feel thirsty, to keep the body's temperature regulation in balance.When working in extreme heat, frequent breaks in shaded or well-ventilated areas should be taken to allow the body time to cool down.
Flame-resistant coveralls made of lightweight material – less warm to wear
These flame-resistant coveralls are tailored for use in hot climates and environments:
- Ensure comfort without compromising safety.
- Lightweight, flexible, and designed to withstand the toughest marine and offshore conditions.
Flame-resistant without wool
Bodyshell is well suited for those who work in hot environments and also need underwear with protection against flames and arc flashes.
Do your work tasks and safety regulations allow you to wear lightweight and breathable work clothing?
HiVis Extreme T-shirt and pique
Both models are made of lightweight bird’s eye polyester, a knitting technique that creates a unique pattern with small holes. This makes the garments extremely lightweight, breathable, and moisture-wicking. The T-shirts feature mesh panels at the neck and under the arms for extra ventilation. Also available in a Curved version for women.
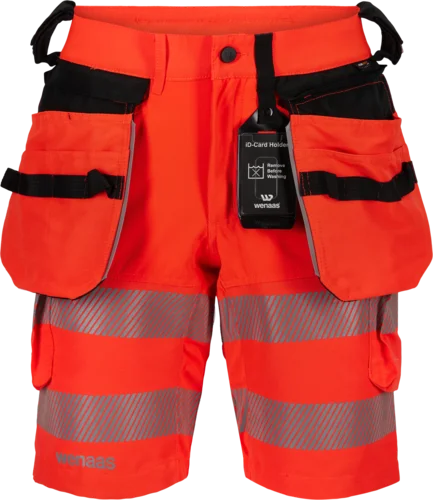
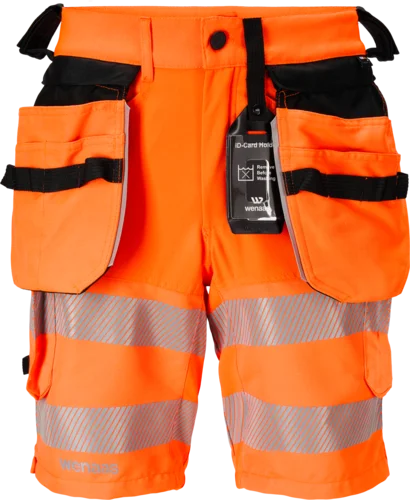
HiVis Extreme - shorts and pirate pants
The shorts and pirate pants are made of stretch fabric for excellent mobility. The pirate pants feature mesh at the back of the legs for extra ventilation, from the bottom reflective strip down. The shorts are a shorter model that reaches mid-thigh. For those who need knee protection, the pirate pants have space for knee pads.
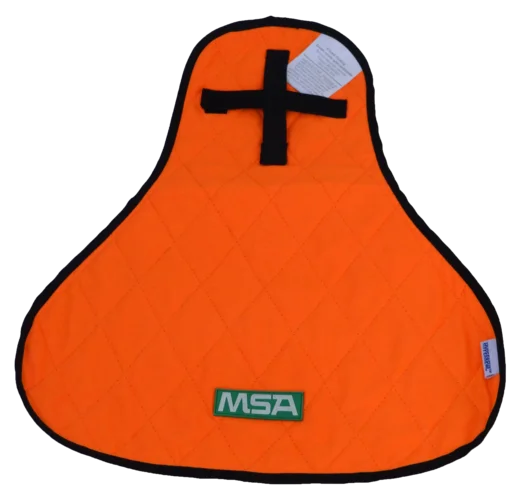
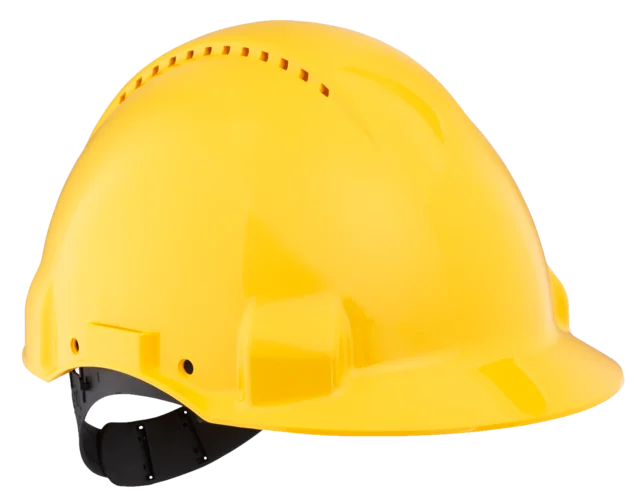
MSA helmets with cooling pad - keep your head cool
MSA offers two innovative cooling pads for MSA helmets. The evaporative cooling technology with HyperKewl™ PLUS reduces the effects of heat stress, enhancing worker safety and productivity. It can lower the temperature under the helmet by up to 12°C. These pads can be used up to 100 times and work by absorbing and releasing water through the multi-layered material.
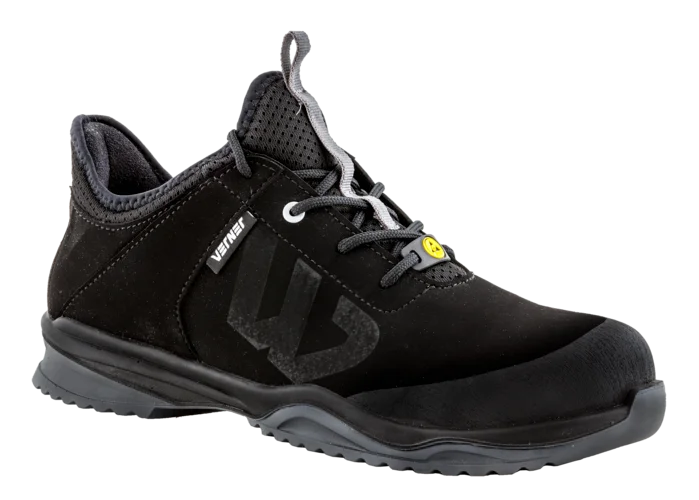
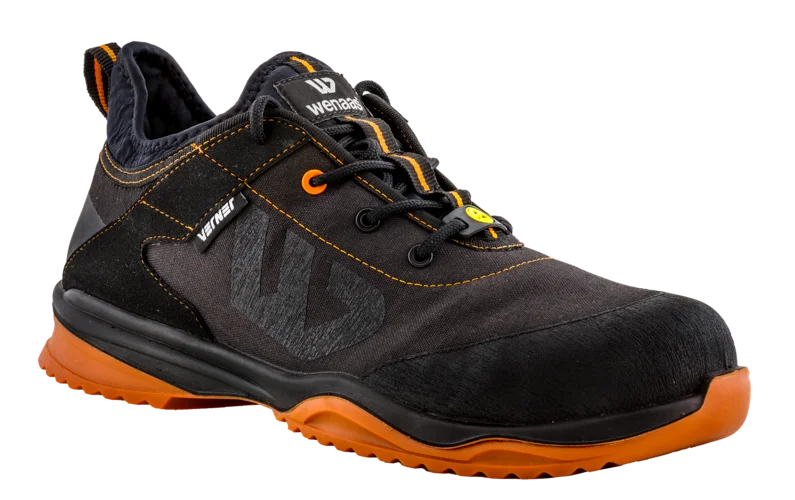
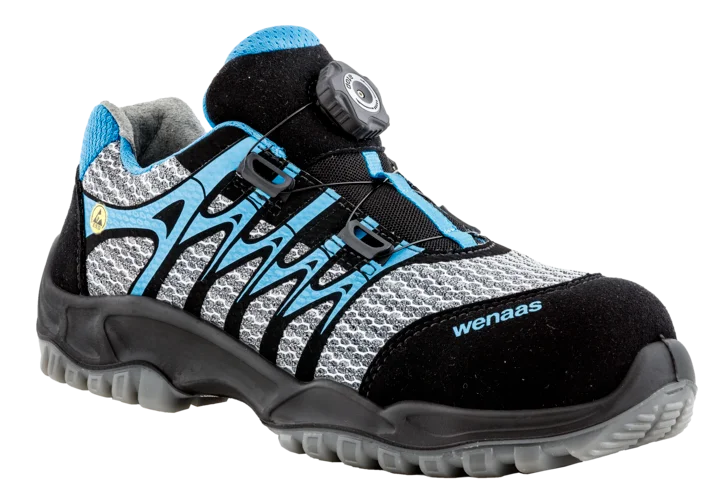
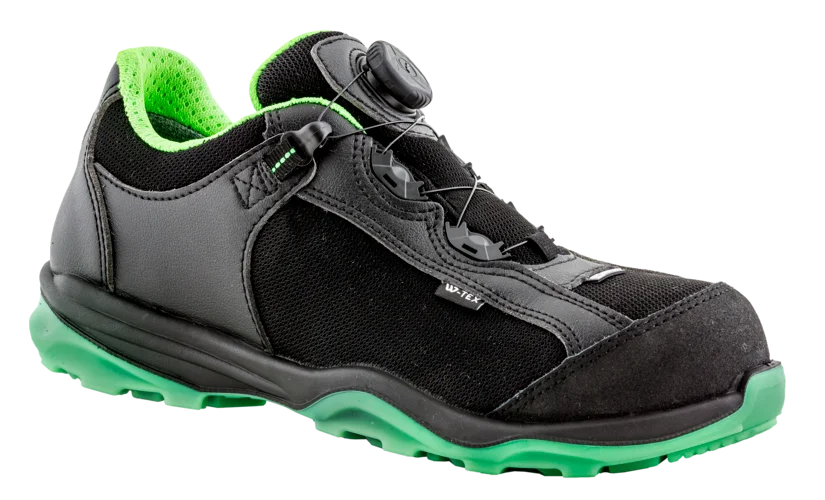
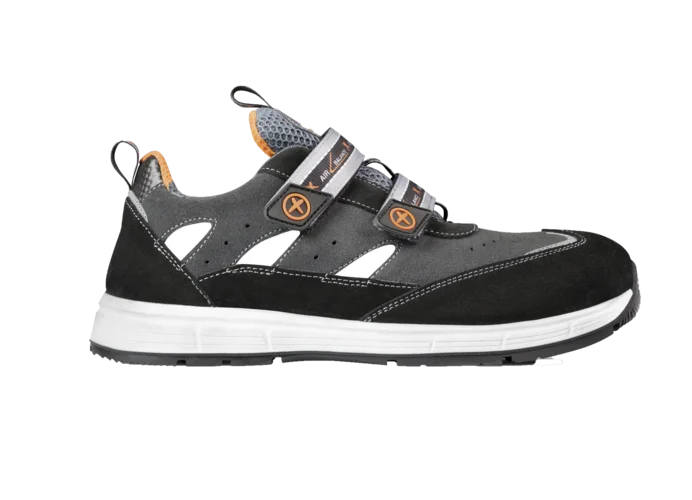
Our breathable safety shoes
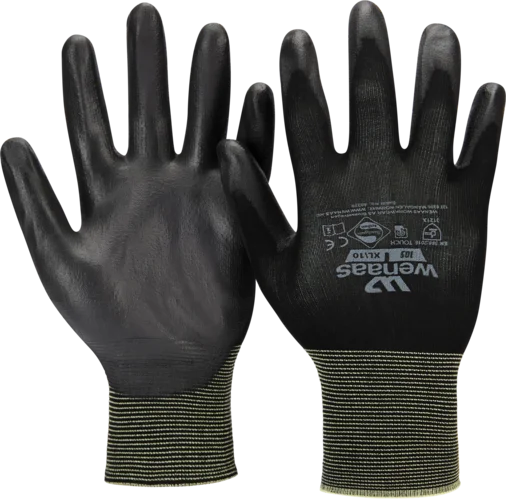
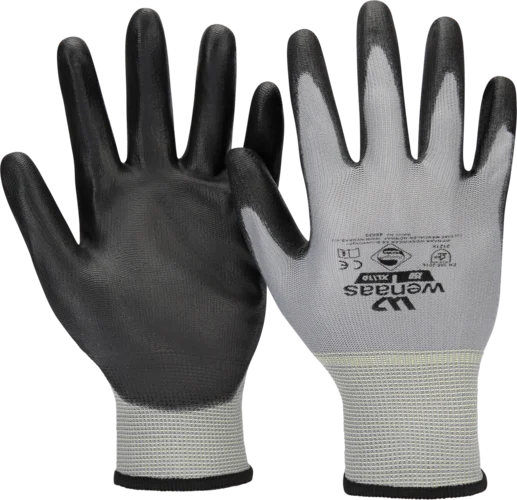
Warm hands when working in hot environments?
Balancing heat is crucial to prevent overheating, especially during physical activity or in high-temperature conditions. Overheating, also known as heat stress, can occur when the body struggles to release excess heat, and highly insulating gloves can contribute to this issue. That’s why it’s important to choose gloves that provide both adequate protection and sufficient ventilation, ensuring comfort without negatively affecting the body’s temperature regulation.When working in hot environments where gloves are necessary, employers should carefully assess the right type of glove based on both safety and heat exposure. Feel free to contact us for guidance in selecting the best option.